- Home
- Company
- Our Services
Odoo Services
ERP Services
- Odoo Apps
- Our Industries
- Locations
- Resources
- Contact us
Call us today!
+91 93422 58771
- Home
- Company
- Our Services
Odoo Services
ERP Services
- Odoo Apps
- Our Industries
- Locations
- Resources
- Contact us
Call us today!
+91 93422 58771
What is ERP System? (Definition of Enterprise Resource Planning)
ERP System comes with a wide range of features and capabilities. It eliminates manual work and makes business processes less error-prone. It provides the capability to get real-time information about various ongoing processes for expense tracking, project planning, seamless integration, and other purposes. It helps decision-makers make strategic decisions based on a single source of truth, optimize resources, reduce costs, and increase profits.Why is ERP System Important?
According to Allied Market Research, the ERP market across the globe is anticipated to reach $117.09 billion by 2030 which clearly indicates an increased CAGR of 10.0% in ten years.ERP software solutions are an integral part of businesses since it accurately plans and coordinates the numerous business functions. One major benefit of ERP solutions for companies is tracking the available inventory along with delivering customer orders.Additionally, it can compare supplier POs and predict demand in the future, thereby guiding companies to make informed decisions.
ERP solution helps the finance department to close the books instantly while the sales team leverages it to streamline all customer orders. Shareholders & the banking sector require ERP for precise financial records that can be developed through the system’s reliable data and analytics.
How Does an ERP System Work?
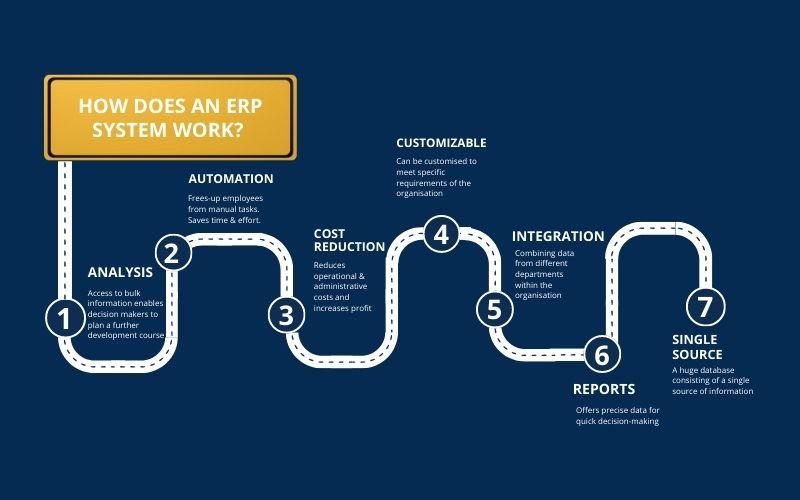
With the ERP system, real-time data can be easily turned into business functions and workflows through all departments. It can deliver outstanding results and ensure on-time delivery and accurate data entry. The ERP vendor can tweak their system to seamlessly integrate their other commonly used solutions, for a cohesive experience.
How Can ERP Improve a Business?
Some prime advantages ERP can offer to businesses involve-
➤ Up-to-date Information
Since ERP applications are consistently receiving data from various departments, it gets updated instantly once the inventory is fetched or a particular shipment is sent to the consumers. It is an added advantage for all decision-makers since they always make a choice depending on the latest available data.
➤ Anytime, Anywhere Data Access
With the ERP system, there is no need to go through a number of paperwork and files. A cloud-based ERP helps warehouse managers to enter data into the warehouse management system, while also analysing patterns and diagnosing the faulty processes that need attention.
➤ Centralised Database
With a centralised database, all decision-makers are on the same platform, since there is no duplicity or conflicting information sources. Additionally, companies shall have the ability to distribute and schedule crucial reports dynamically. You can also easily get access to the detailed information once you generate detailed reports based on it.
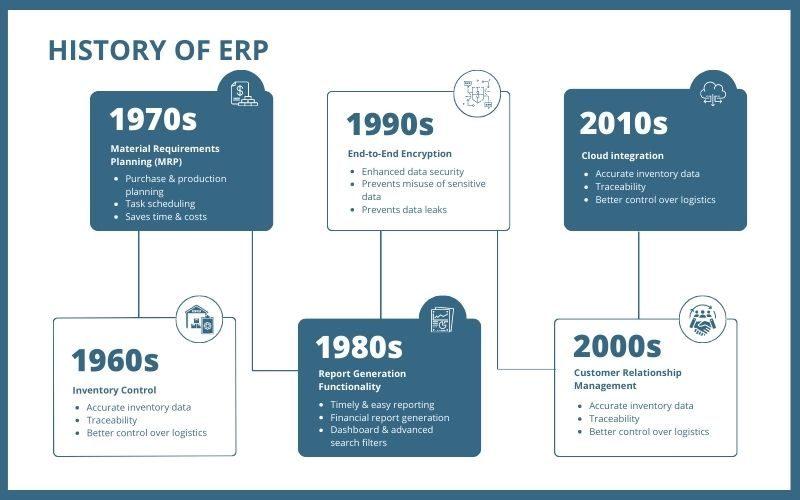
History of ERP
The history of ERP dates back 100 years with the development of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), a paper-based manufacturing system in 1913. During the period of 1964-1990, EOQ was transformed into an advanced system, Material Requirements Planning (MRP), which provided advanced capabilities. In the 1990s, a full-fledged ERP was developed with modern capabilities.